Fosun Pharma’s Self-developed Drug, Luvometinib (FCN-159), Presented Updated Data at the ASCO Annual Meeting
The updated data of efficacy and safety of Luvometinib (FCN-159), a self-developed innovative drug by Fosun Pharma, in pediatric participants with neurofibromatosis type 1 from a phase 2 study was presented in the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting on May 22, 20251.
Luvometinib Tablet (Chinese trade name:复迈宁®), a highly selective MEK1/2 inhibitor, was officially approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) on May 29, 2025, after being granted multiple breakthrough therapy and priority review designations. The approved indications are for the treatment of adult patients with Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) and histiocytic neoplasms and for the treatment of pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection.
Based on the Phase 1/2 study data presented at the 2023 and 2024 ASCO annual meetings, this update includes the latest follow-up data on efficacy and safety, demonstrating the positive clinical benefits and favorable safety profile of Luvometinib, further providing evidence for the scientific use of Luvometinib.

Focusing on the plight of children with NF1 and filling the therapeutic gap
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder with a clear familial inheritance pattern, often involving multiple systems. Approximately 30%-50% of patients are accompanied by plexiform neurofibroma (PN), which can lead to disfigurement, pain, dysfunction, and other severe problems, significantly affecting the patient's quality of life. PN mostly develops in childhood, and the progression is quite rapid during this critical period of growth and development, making the therapeutic needs for children with NF1-PN particularly urgent2.
Although surgery is currently the main therapeutic approach for NF1-associated PN, only about 15% cases can achieve complete tumor excision, and PN re-growth occurs in 43% of those who underwent partial or subtotal resection due to the tumor originating from nerves3. Treatment options are extremely limited for patients with unresectable or recurrent PN patients, especially for 2-year-old pediatric patients in China, as there were no drugs available before the approval of Luvometinib.
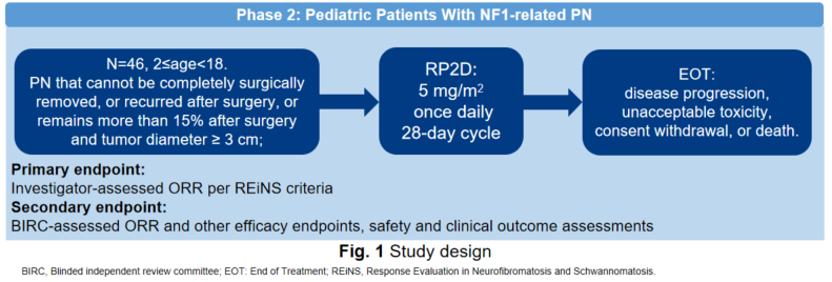
This study is a multicenter, open-label phase 2 clinical trial, aiming to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Luvometinib (FCN-159) in treating NF1-associated PN in pediatric patients. The primary endpoint is the objective response rate (ORR) evaluated by investigators (INV). The key secondary endpoint is the ORR evaluated by the Blinded Independent Review Committee (BIRC).
Luvoxmetinib has a rapid onset of action and marked response, with an ORR of 60.5% and a median time to response of 4.7 months
As of September 23, 2024, 46 pediatric patients (aged 2-17) with NF1-associated PN were enrolled in this multicenter, open-label phase 2 clinical study and received Luvoxmetinib at a dose of 5 mg/m2once a day. The median follow-up was 25.1 months.
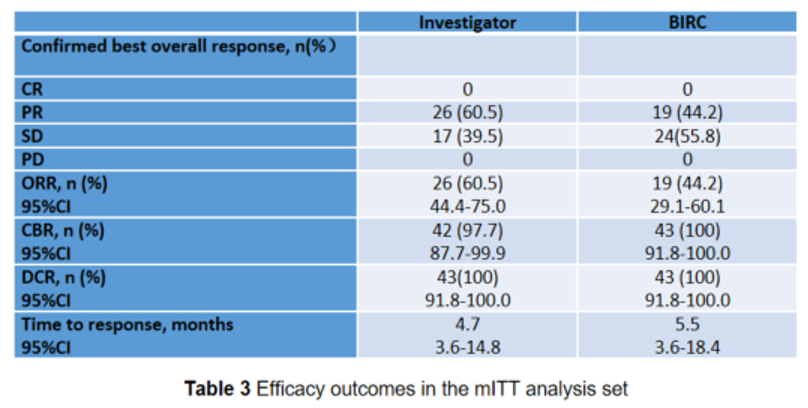
Among the 43 evaluable patients, the ORR assessed and confirmed by INV reached 60.5% (95% CI: 44.4-75.0), with 26 cases achieved partial response (PR), 17 cases had stable disease (SD), and no case had progression disease (PD). The median duration of response (DOR) and median progress free survival (PFS) were not reached.
Among the 43 evaluable patients, the ORR assessed and confirmed by BIRC was 44.2% (95% CI: 29.1-60.1), with 19 cases had PR, 24 cases had SD, and no patient experienced PD.
The median time to response assessed by investigators was 4.7 months, while the median time to response assessed by BIRC was 5.5 months.
Among patients with a baseline NRS ≥ 2, 92.9% experienced significant pain improvement
Among the 14 assessable patients with pain (i.e., those with a baseline overall tumor pain score of ≥ 2 and at least one post-baseline evaluation), the mean change in overall pain intensity compared to baseline was -3.5 points. 13 patients (92.9%) achieved a pain score reduction ≥ 2 compared to baseline, which was considered clinically meaningful, and 11 patients (78.6%) rated at 0, indicating pain disappeared.
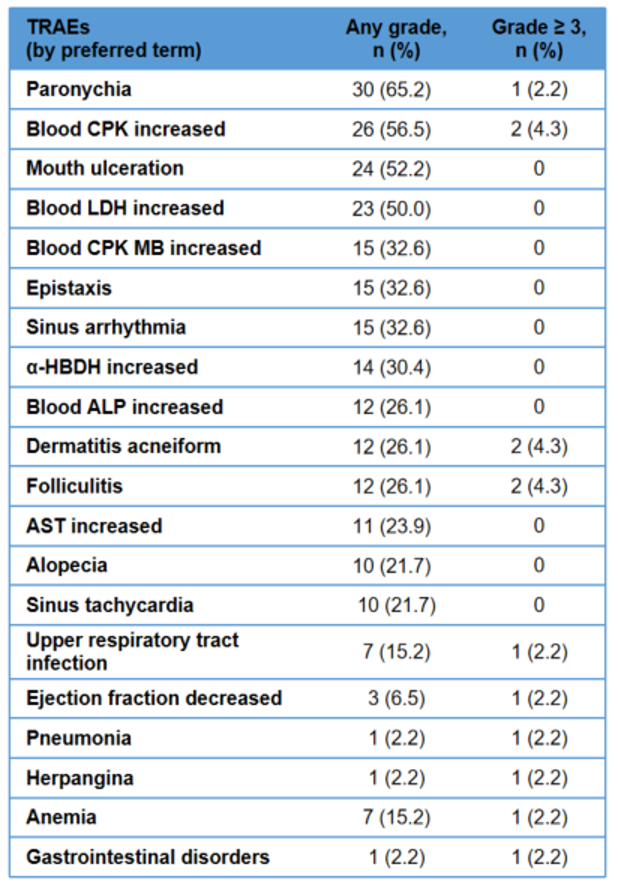
Adverse events were mostly grade 1-2 and controllable, indicating favorable safety with no new safety signals
The incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was 97.8%. TRAEs happened predominantly in grades 1-2, with grade ≥ 3 TRAEs accounting for only 21.7%. Common adverse events mainly included paronychia (65.2%), increased blood creatine phosphokinase (CPK) (56.5%), mouth ulceration (52.2%), and increased blood lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (50%), all of which are common and controllable responses associated with MEK inhibitors.
The frequency of abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting ranged from 2.2% to 19.6% and none at grade≥3. Only 2 cases (4.3%) reported treatment-related serious adverse events (one case of dermatitis acneiform and pneumonia each). TRAEs led to dose interruption in 13 patients (28.3%). None led to dose reduction, discontinuation or death. Patient compliance reached 100%.
The safety of Luvoxmetinib is consistent with the known safety data of MEK inhibitors, and adverse events can be effectively managed through symptomatic treatment and discontinuation of the drug. It is well tolerated in children and adolescents.
Metabolic stability, high selectivity, and low toxicity characteristics bring clinical benefits to Chinese NF1 pediatric patients
As the first domestically developed MEK inhibitor, Luvoxmetinib achieves advantages such as metabolic stability, high selectivity, low toxicity, and an extended half-life through synergistic design in its structure. Its pharmacokinetic characteristics support once-daily drug administration, unaffected by food and fewer interactions with co-administered drugs, which contribute to better compliance and suitability for long-term use in children. Luvoxmetinib not only overcomes the limitations of traditional therapy with its highly selective mechanism but also brings significant tumor remission rates and pain improvement, offering positive clinical benefits for children with NF1.
In addition, Luvoxmetinib is at the stage of Phase III clinical trial in mainland China for the treatment of adults with neurofibromatosis type 1, and at the stage of Phase II clinical trials in mainland China for the treatment of low-grade glioma, extracranial arteriovenous malformations, children with langerhans cell histiocytosis. Luvoxmetinib has been granted breakthrough therapy designation by the Center for Drug Evaluation of the NMPA for the treatment of two indications of adults with inoperable or post-operative residual/recurrent NF1-associated PNs and children with langerhans cell histiocytosis. Fosun Pharma will continue to advance the development of Lovemetinib for other indications and benefit more patients.
*This material is professional medical information and for healthcare professionals only. For specific diagnostic and treatment information, please consult physicians and follow the medical advice.
References:
1.JinHu Wang et al. JCO 43, 10044-10044 (2025).
2.China Rare Disease Alliance Type I Neurofibromatosis Multidisciplinary Diagnosis and Treatment Collaboration Group. [J]. Rare Disease Research, 2023, 2(2): 210-230.
3.Fisher MJ, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24(11):1827-1844

